Personal hygiene has improved significantly over the past century, but the problem of worms is still not only associated with rural dwellers, but also urban dwellers. Statistics clearly show how high the risk of infection with a worm invasion is: every third of people on the planet suffer from helminthiasis. But the manifestations of the disease are not always clear, and in some cases, patients cannot interpret symptoms correctly and remain in the dark for long periods of time without taking any action. Helminthiasis and other diseases with similar symptoms present questions about how to know you have worms.

Worms are a wide range of parasitic worms and the main signs of their presence in the human body are similar to each other. Doctors believe that everyone has been exposed to helminthiasis at least once in their lifetime. In addition, the presence of worms in the body can trigger the development of other diseases, sometimes very dangerous, so the problem of diagnosing this disease is very important.
Infection mechanism
There are four main ways of worm infection:
- water, dirt or sand. Soil and water provide ideal conditions for parasite egg storage. People bathing in open water are always at risk of swallowing eggs, which then turn into adults. Not as rare as it seems, people also swallow dirt particles, putting themselves at risk of infection. Certain types of parasites can enter the body directly through the skin.
- food.Unwashed or cooked fruits and vegetables may have eggs on their shells. The risk of eating raw or lightly processed meat, dried fish, dairy products, etc. is not low.
- contact with patients. Direct contact with both sick and infected animals is possible. Common activities, living in common areas, and close communication help parasites enter the gut quickly and develop further.
- bites.Worms can be spread through insect bites. This is one of the rarest forms of infection in temperate regions, but it can sometimes be the cause of disease. This route is more common in hot countries and should be kept in mind when going on vacation to warmer places.
symptom
For those of you wondering how to know you have worms, you should understand the principles of recognizing symptoms. Any symptoms of helminthiasis do not appear immediately after infection, but only when the parasite stops migrating through the gastrointestinal tract and begins to develop into an adult.
Some signs are due to ingestion of toxins released by the worm during its life. All wastes enter the intestinal lumen, from where they are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to all organs. Often in the case of multiple infections, symptoms are more numerous and stronger when the number of worms becomes significant. In people who are immunosuppressed or have other chronic diseases, symptoms worsen over a relatively short period of time.

All signs fall into two broad categories: overt and covert. Explicit can be independently assessed at home, while implicit can only be determined on an outpatient basis by appointments for certain tests and examinations.
explicit
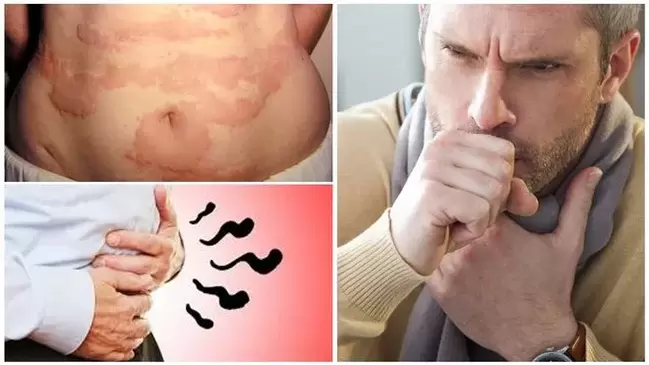
Obvious symptoms include those in which the worm is understandably present in the body. Their presence does not cause too obvious symptoms, for example, as the virus develops. The parasite targets life in the body, so an infected host's condition deteriorates too much to be life-threatening. Therefore, these symptoms do not require urgent care.
You can suspect or understand the presence of a worm infestation by the following signs:
- Gradual weight loss for no apparent reason that lasts for months, sometimes years. The rate of weight loss is not catastrophic, usually 2-5% per month. Due to the high intensity of infection in people with weakened immunity, this number can reach 10%.
- Gastrointestinal disease. Some worms can block the bile ducts or intestinal lumen, causing stable constipation. Conversely, with the high-intensity release of the toxin, recurrent diarrhea may occur. Increased flatulence and gas formation are often observed due to inflammation of the upper wall of the small intestine, and bloating may occur.
- Severe pain in joints and muscles. This manifestation is usually attributed to the development of arthropathy, but in the case of helminths, it is caused by the migration of parasites. Additionally, this pain may be due to the effects of toxins on joints and muscle tissue.
- Itching near the anus. This phenomenon is caused by a large number of species of parasites crawling out of the rectal cavity to reproduce and lay eggs. This causes intense itching that tends to get worse at night and at night.
- Allergic manifestations. It usually occurs due to the presence of large amounts of toxins in the blood or due to damage to the intestinal mucosa, which can lead to an increased immune system and allergic reactions.
- Pulmonary manifestations. The possibilities are wide ranging, from a persistent cough to ending with pneumonia. Characteristic of intense ascariasis occurring within not less than three months from the date of infection.
- temperature rises. This manifestation can have different strengths. In most cases, low temperatures of around 37°C persisted around the clock, but in rare cases a fever could be observed.
hidden
Hidden signs can only be revealed by a doctor who can adequately assess the clinical situation and understand why the worms might be the likely cause. Precautions for the diagnosis of helminthiasis are:
- Fecal analysis of worms. It must be submitted in two stages, therefore, experts do not consider the results of an analysis to be reliable. This is due to the periodicity of reproduction, so it is not always possible to understand that a patient has worms from an analysis of the stool.
- Clinical blood test. Elevated levels of eosinophils may indicate the presence of parasites in the body. Such assumptions often arise after testing during the treatment or diagnosis of other diseases.
- Antibody Analysis. Currently, it is one of the most reliable diagnostic methods for knowing if a person has worms. Although it is more expensive than similar drugs, doctors are more and more fond of prescribing it recently because of its high informativeness and reliability.
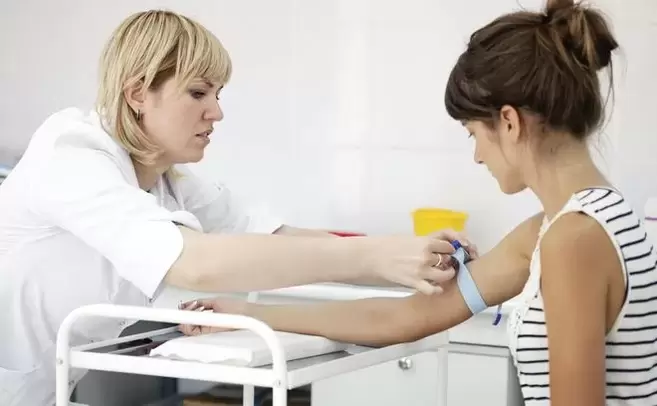
Antiparasitic medications or laxatives should not be taken before any clinical trials for the parasite have been conducted, as this can make diagnosis difficult.
sign of a child
In children, the presence of worms is more easily diagnosed than in adults. Poor hygiene, close contact with livestock or street animals, and an underdeveloped immune system contribute to this. Growing organisms are often more responsive to the presence of parasites, and the consequences can be more widespread than in adults. But it's not easy to understand that a child has bugs. Symptoms may be the same as in adults, but are usually more severe.
In most cases, the signs that a worm has invaded a child are:
- Lose weight fast. With running pictures, such performance will lead to a delay in physical development;
- Degeneration of hair and nails. It is caused by chronic deficiencies of nutrients and vitamins due to disrupted absorption of digested food in the gut.
- sleep disorder. Pathology can cause children to wake up more frequently during the night and cry, whirl and talk in their dreams.
- irritability. Nervous system toxicity and poor health can affect a child's emotional state, resulting in increased excitability, caprices, tearing, and more.
- The desire to constantly scratch the anus. Children have no control over their outward appearance, so this symptom often helps to understand the cause of disease and physical changes.
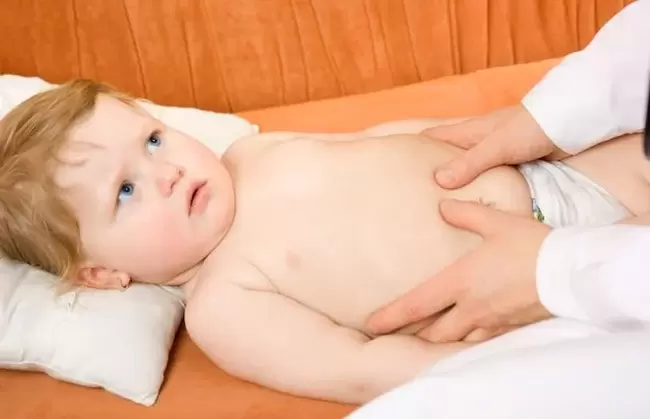
Some parents prefer to give their children broad-spectrum antiparasitic drugs for prophylaxis, but experts do not recommend this because most of these drugs are difficult to tolerate. It's best to first find out if your child is infected and what kind of treatment is needed, as treatments vary significantly for different types of worms and are not always effective for other groups of worms.






































